Choose all statements that accurately describe animal gap junctions. – Animal gap junctions, as the title suggests, are captivating structures that accurately describe animal gap junctions. Delving into their intricate world unveils a fascinating tale of intercellular communication and coordination, orchestrated through these remarkable channels. Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey as we unravel the secrets of animal gap junctions, their structure, function, regulation, and significance.
Gap junctions are not mere bystanders in the cellular landscape; they are dynamic gateways that facilitate the seamless exchange of ions, molecules, and signals between neighboring cells. Their presence ensures that cells within tissues and organs function in harmony, maintaining homeostasis and orchestrating coordinated responses.
Structure of Animal Gap Junctions: Choose All Statements That Accurately Describe Animal Gap Junctions.
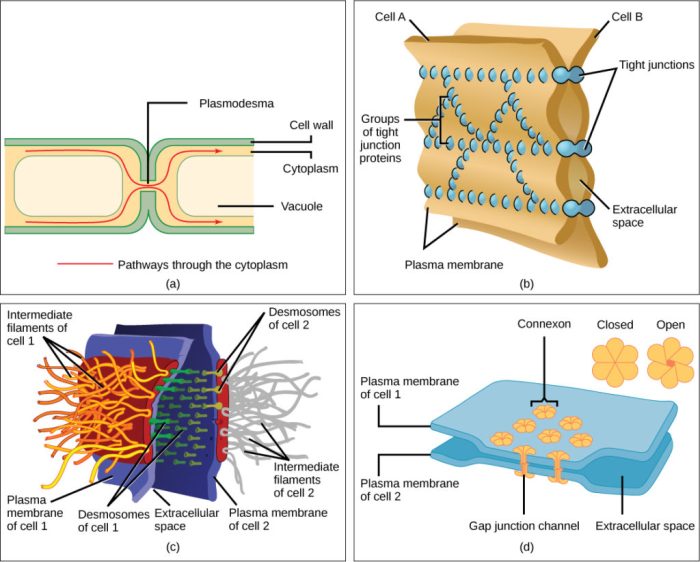
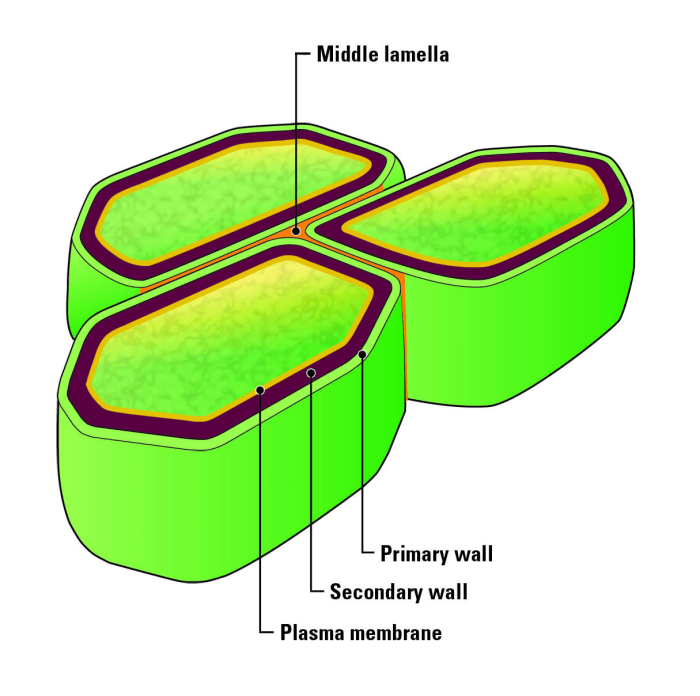
Animal gap junctions are specialized structures that allow direct communication between adjacent cells. They consist of two closely apposed plasma membranes with a narrow extracellular space between them, known as the gap.
Each gap junction is composed of two hemichannels, one from each cell, which dock together to form a pore. The hemichannels are composed of six connexin proteins, which form a transmembrane channel.
The following diagram shows a detailed structure of a gap junction:
- Plasma membrane:The outer boundary of each cell.
- Extracellular space:The narrow gap between the plasma membranes.
- Hemichannel:A protein complex that forms one half of a gap junction.
- Connexin protein:A transmembrane protein that forms the pore of a hemichannel.
Function of Animal Gap Junctions, Choose all statements that accurately describe animal gap junctions.
Gap junctions play a critical role in cell-to-cell communication. They allow the exchange of ions, molecules, and signals between cells, facilitating the coordination of cellular activities and tissue homeostasis.
- Electrical coupling:Gap junctions allow the passage of ions, enabling the spread of electrical signals between cells. This is essential for rapid communication in excitable tissues, such as the heart and nervous system.
- Metabolic coupling:Gap junctions facilitate the exchange of small molecules, such as nutrients, metabolites, and waste products. This allows cells to share resources and maintain a stable internal environment.
- Signal transduction:Gap junctions allow the passage of signaling molecules, such as second messengers and hormones. This enables the coordinated regulation of cellular processes within a tissue.
Regulation of Animal Gap Junctions
The opening and closing of gap junctions are tightly regulated to control the flow of ions and molecules between cells.
- Electrical signals:Gap junctions can be opened or closed by changes in the electrical potential across the plasma membrane.
- Chemical signals:Gap junctions can also be regulated by chemical signals, such as calcium ions and neurotransmitters.
- Phosphorylation:The phosphorylation of connexin proteins can affect the permeability of gap junctions.
Importance of Animal Gap Junctions
Gap junctions are essential for the proper function of many tissues and organs. They play a crucial role in:
- Electrical conduction:Gap junctions allow the rapid spread of electrical signals in the heart and nervous system.
- Tissue coordination:Gap junctions facilitate the exchange of nutrients, metabolites, and signals between cells, ensuring coordinated tissue function.
- Homeostasis:Gap junctions allow cells to share resources and maintain a stable internal environment.
Abnormal gap junction function can lead to various diseases and conditions, such as cardiac arrhythmias, neurological disorders, and skin diseases.
Gap junctions are also potential therapeutic targets for a range of diseases. By modulating gap junction function, it may be possible to treat diseases that are caused by abnormal cell-to-cell communication.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the primary function of animal gap junctions?
Animal gap junctions primarily facilitate the direct exchange of ions, molecules, and signals between adjacent cells, enabling rapid and coordinated cellular communication.
How do gap junctions contribute to tissue coordination?
Gap junctions allow for the rapid and efficient spread of electrical and chemical signals within tissues, ensuring synchronized responses and maintaining tissue homeostasis.
What factors can influence the permeability of gap junctions?
The permeability of gap junctions is influenced by various factors, including electrical and chemical signals, pH, and the presence of specific molecules or drugs.