Embark on a fascinating journey through the human body with our comprehensive cavities of the body quiz. This immersive experience delves into the intricate network of cavities that house and protect our vital organs, revealing their functions and clinical significance.
From the spacious thoracic cavity to the protective cranial cavity, our bodies are meticulously organized into specialized compartments, each with a unique role to play in maintaining our well-being. Discover the organs that reside within these cavities and the essential systems they support.
Types of Body Cavities
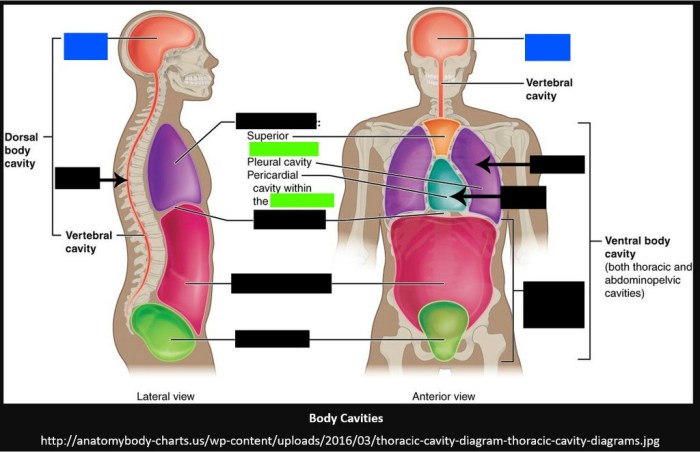
The human body is made up of several cavities, each of which contains specific organs and structures. These cavities provide protection, support, and organization for the body’s internal components.
Taking a cavities of the body quiz can be a fun way to test your knowledge of human anatomy. If you’re looking for more information on this topic, you may want to check out the case of Heath v. Swift Wings Inc.
. This case involved a dispute over whether an airline was liable for injuries sustained by a passenger who fell and hit her head on the armrest of her seat. The court’s decision in this case provides some interesting insights into the legal responsibilities of airlines to their passengers.
After reading about the case, you can return to your cavities of the body quiz and continue testing your knowledge.
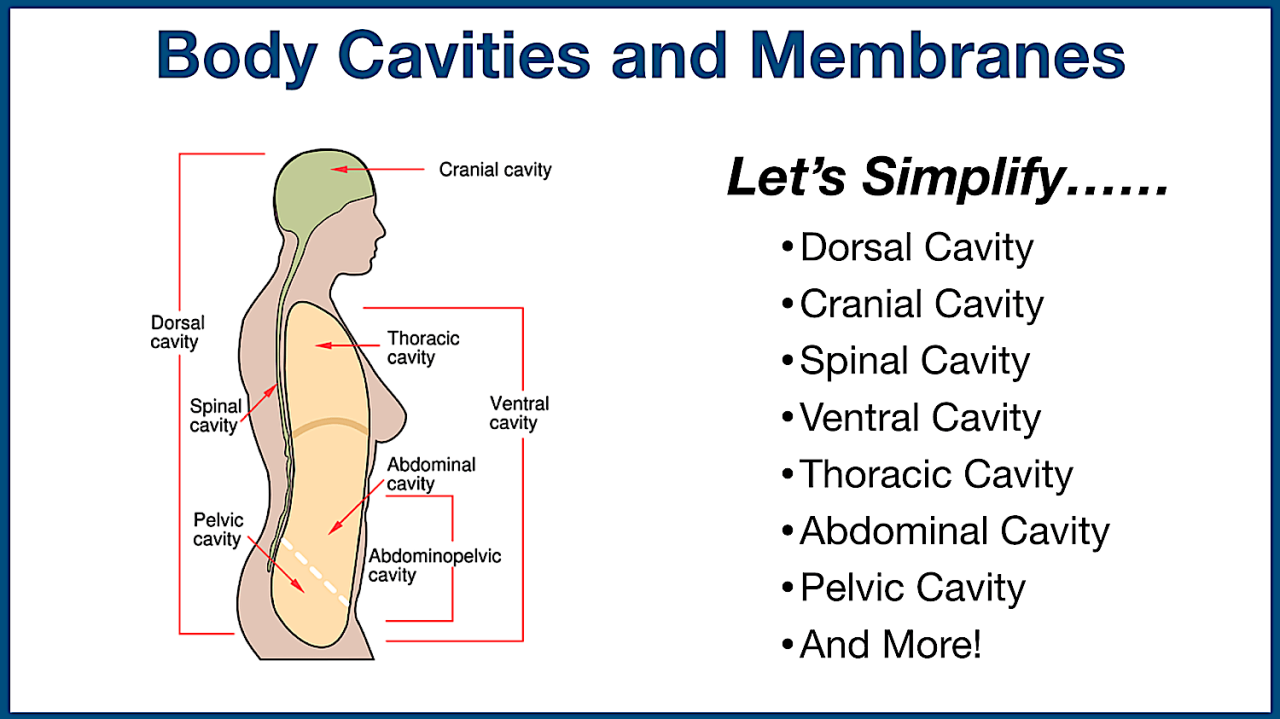
There are two main types of body cavities: the dorsal cavity and the ventral cavity.
Dorsal Cavity
The dorsal cavity is located in the back of the body and is further divided into two subdivisions:
- Cranial cavity: Contains the brain and is located within the skull.
- Spinal cavity: Contains the spinal cord and is located within the vertebral column.
Ventral Cavity
The ventral cavity is located in the front of the body and is also divided into two subdivisions:
- Thoracic cavity: Contains the heart, lungs, esophagus, and other structures, and is surrounded by the rib cage.
- Abdominopelvic cavity: Contains the abdominal and pelvic organs, including the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and reproductive organs.
Functions of Body Cavities
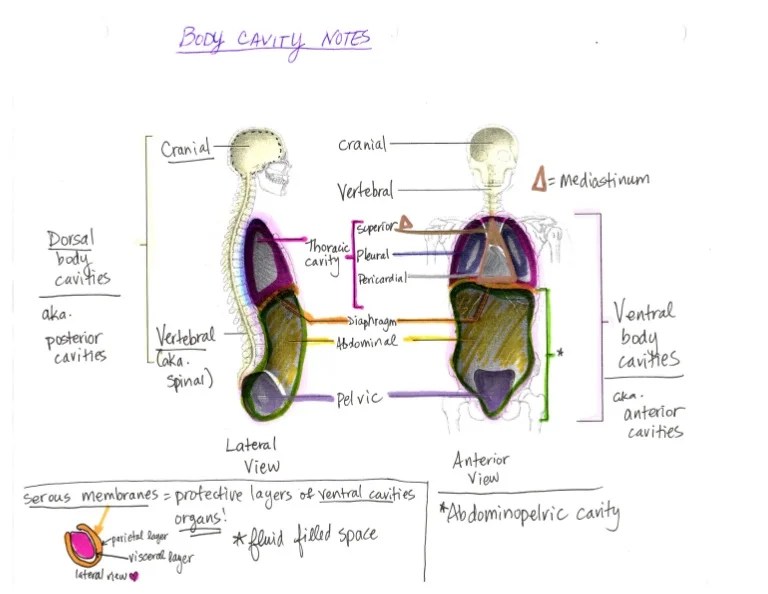
Body cavities play a crucial role in maintaining the proper functioning of organs and tissues. They provide a protected environment, support, and facilitate communication between different organ systems.
Protection and Support, Cavities of the body quiz
Body cavities offer protection to vital organs from external impacts, trauma, and mechanical stress. The bones, muscles, and connective tissues surrounding the cavities create a protective barrier that shields the organs from damage. Additionally, the fluid-filled cavities provide cushioning and support, preventing organs from shifting or being displaced.
Organs Located in Body Cavities
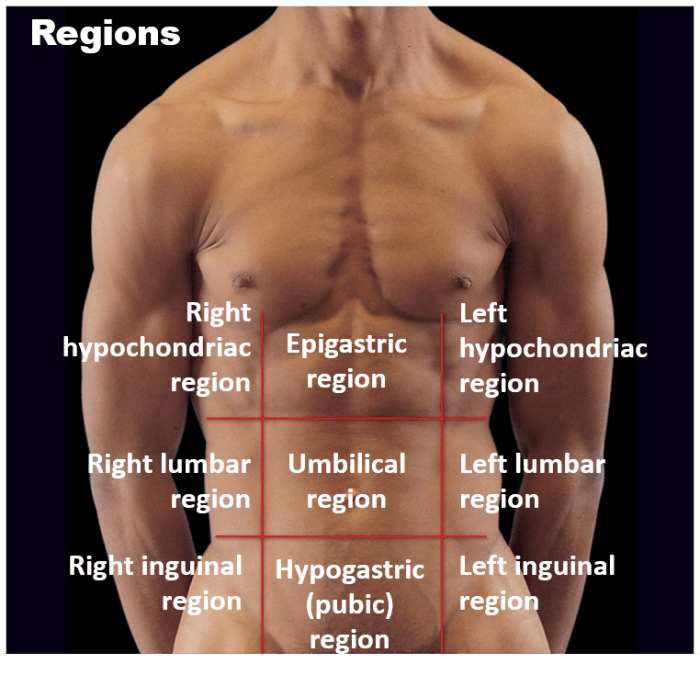
The organs within the body are organized into various cavities, each with specific functions and associated systems.
The following table provides an overview of the organs located in each body cavity, their functions, and the systems they belong to:
Body Cavity, Organs Located in Cavity, Function of Organs, Associated Systems
| Body Cavity | Organs Located in Cavity | Function of Organs | Associated Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cranial Cavity | Brain, Cerebellum, Medulla oblongata | Controls body functions, thoughts, emotions | Nervous system |
| Spinal Cavity | Spinal cord | Transmits signals between brain and body | Nervous system |
| Thoracic Cavity | Heart, Lungs, Esophagus, Trachea | Pumping blood, Gas exchange, Food passage, Air passage | Cardiovascular system, Respiratory system, Digestive system |
| Abdominal Cavity | Stomach, Liver, Pancreas, Small intestine, Large intestine | Food digestion, Nutrient absorption, Waste elimination | Digestive system |
| Pelvic Cavity | Bladder, Reproductive organs | Urine storage, Reproduction | Urinary system, Reproductive system |
Body Cavities and Body Planes
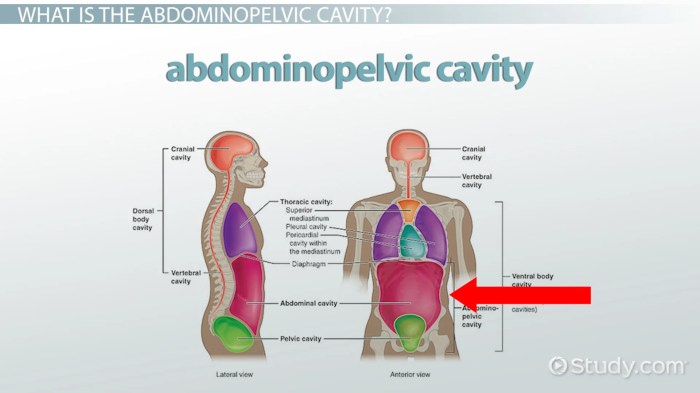
Body cavities and body planes are closely related concepts that help us describe the location and orientation of structures within the body. Body cavities are the fluid-filled spaces that house internal organs, while body planes are imaginary lines or surfaces that divide the body into different sections.
Body planes help define the location of organs within cavities. The three main body planes are the sagittal plane, the coronal plane, and the transverse plane. The sagittal plane divides the body into left and right halves, the coronal plane divides the body into front and back halves, and the transverse plane divides the body into upper and lower halves.
Relationship between Body Cavities and Body Planes
The relationship between body cavities and body planes is that the cavities are located within the planes. For example, the thoracic cavity is located within the sagittal and coronal planes, and the abdominal cavity is located within the coronal and transverse planes.
Body planes can also be used to describe the location of organs within cavities. For example, the heart is located in the thoracic cavity, anterior to the sagittal plane and superior to the transverse plane.
Clinical Significance
Understanding the relationship between body cavities and body planes is important for a number of reasons. For example, it helps medical professionals to accurately locate organs during surgery and to diagnose injuries.
Clinical Significance of Body Cavities
Body cavities are clinically significant as they provide a framework for organizing and locating organs and structures within the body. Understanding these cavities aids in medical diagnosis and treatment, enabling healthcare professionals to accurately assess and address various medical conditions.
The body cavities act as compartments, separating and protecting vital organs from external factors and providing support and cushioning. The presence of fluid within some cavities, such as the pleural and pericardial cavities, reduces friction and facilitates organ movement. Furthermore, the body cavities allow for the passage of nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels, ensuring proper communication and nourishment of organs.
Diagnostic Significance
- Physical Examination:Palpation and auscultation of body cavities can reveal abnormalities, such as fluid accumulation, organ enlargement, or masses, indicating underlying medical conditions.
- Imaging Techniques:X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs provide detailed images of body cavities, allowing for visualization of organs, detection of abnormalities, and assessment of their extent.
- Endoscopy:Endoscopic procedures, such as laparoscopy and colonoscopy, enable direct visualization and examination of the interior of body cavities, aiding in diagnosis and treatment.
Therapeutic Significance
- Surgery:Surgical interventions often involve accessing body cavities to repair damaged tissues, remove diseased organs, or perform diagnostic procedures.
- Fluid Drainage:In cases of fluid accumulation within body cavities, such as pleural effusions or ascites, drainage procedures can be performed to alleviate symptoms and improve organ function.
- Radiation Therapy:For certain types of cancer, radiation therapy may be delivered directly to specific body cavities, targeting affected organs while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
FAQ Insights: Cavities Of The Body Quiz
What are the main types of body cavities?
The two main types of body cavities are the dorsal cavity and the ventral cavity.
What organs are located in the thoracic cavity?
The thoracic cavity houses the heart, lungs, and esophagus.
What is the function of the peritoneal cavity?
The peritoneal cavity lines the abdominal cavity and contains the digestive organs.